Giorgia Guglielmi
Giorgia Guglielmi is a freelance science writer based in Basel, Switzerland. Specializing in life sciences, medicine, and the relationship between science and society, she has published numerous articles in outlets including Nature, Science, and Scientific American. She holds a PhD in biology from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and a Master’s in Science Writing from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She has received recognition for her work, including the John Kendrew Award in 2020 and an ERC-funded FRONTIERS Media Fellowship in 2025. She has also led lectures and workshops on science communication at institutions such as Harvard University and the University of Zurich.
Gastroenterology
Researchers have found that β-carotene modifies the abundance of certain gut microbes and improves the intestinal dysfunctions
Immunology, Oncology
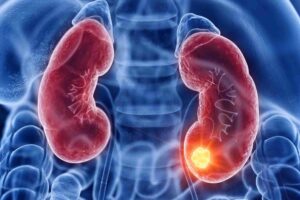
Researchers have found that combining a probiotic product with immunotherapy may boost anti-tumor responses in people with advanced kidney cancer.
Dermatology
Researchers have found that Lactobacilli could be used to treat common acne lesions, reducing the need for topical antibiotics.
Neuroscience
Researchers have found that some gut microbes may be connected to depression, thus highlighting that the intricate relationship between humans and their microbiota could have important health implications.
Gastroenterology
Researchers have now found that the interactions between existing gut commensals sets the odds for whether new microbes are acquired.
Neuroscience
Researchers have found that testosterone-degrading enzymes expressed by gut microbes are associated with depressive symptoms.
Scientific research
Researchers have found that microbes in the gut of ground squirrels recycle a waste product into building blocks to make proteins, helping the animals to survive a long winter without…
Oncology
Akkermansia can be used as a biomarker to identify who is likely to respond to treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. A new study published in Nature Medicine claims
Scientific research
By combining HiFi with advanced algorithms, the researchers identified the genomes of 428 microbial species with more than 90% completeness.
Pediatrics, Pneumology
Early viral encounters are associated with disadvantageous immune and microbiota profiles, as well as recurrent respiratory infections. A new study published in Nature Microbiology claims.