Giorgia Guglielmi
Giorgia Guglielmi is a freelance science writer based in Basel, Switzerland. Specializing in life sciences, medicine, and the relationship between science and society, she has published numerous articles in outlets including Nature, Science, and Scientific American. She holds a PhD in biology from the European Molecular Biology Laboratory and a Master’s in Science Writing from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. She has received recognition for her work, including the John Kendrew Award in 2020 and an ERC-funded FRONTIERS Media Fellowship in 2025. She has also led lectures and workshops on science communication at institutions such as Harvard University and the University of Zurich.
Oncology
Some gut microbial metabolites boost the efficacy of antitumor drugs by regulating the body’s immune response and could be used as a part of cancer therapy.
Gastroenterology, Immunology
Microbial transplants could be used as a non-invasive and safe strategy to manipulate the gut microbiota, which has been linked to HIV infection.
Gastroenterology
Common gut fungi called Debaryomyces hansenii can influence the severity of Crohn’s disease and other inflammatory bowel diseases.
Pediatrics
Microbial and fungal communities interactions shape the gut microbiota in preterm babies. The findings could help to develop microbiota interventions.
Gastroenterology, Neuroscience
The alterations in gut microbial composition could play a role in the gastrointestinal complications associated with Parkinson’s disease.
Dermatology, Scientific research
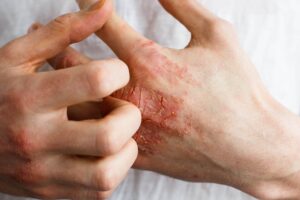
A bacterial strain, called Staphylococcus hominis A9, inhibited the expression of a S. aureus toxin that promotes inflammation in atopic dermatitis.
Nutrition
The gut microbiota make-up could determine whether a person will benefit from the beneficial effects of the Mediterranean diet.
Oncology
Probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium can activate a person’s immune system and improve the response to some anti-cancer therapies.
Scientific research
The way gut bacteria increase their access to nutrients by adhering to food particles, could advance the development of microbiota-based diagnostics.
Scientific research
The Gut Phage Database, within more than 140,000 viral species, is a blueprint to guide ecological and evolutionary analysis in future virome studies.