Overview
Events, Dermatology
Imbalances of microbes, which are normally present on the skin, are one of the main subjects raised during the 24thCongress of Dermatology.
Dermatology
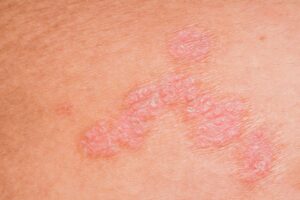
Scientists have traced how the interplay of different species of Staphylococcus bacteria on the skin could influence the severity of skin eczema.
Immunology
A commensal Lactobacillus strain worsens the symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus and triggers the host's immune system.
Immunology
The gut microbiota reduces the production of retinoic acid, a metabolite of vitamin A, to regulate immune activity and prevent pathogens.