skin microbiota
Dermatology, Video
Sarah Lebeer (Research professor, University of Antwerp) described how she and her colleagues developed a new probiotic topic formulation to treat Acne.
Dermatology, Scientific research
The findings of a recent study suggest that dengue and Zika viruses are able to change their host’s odor by altering the skin microbiota.
Dermatology, Oncology
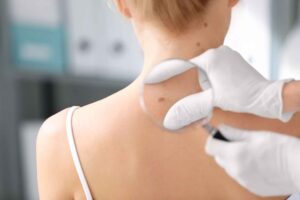
The findings could help to develop microbiota-based strategies to advance immunothery treatments for melanoma.
Dermatology
Researchers have found that Lactobacilli could be used to treat common acne lesions, reducing the need for topical antibiotics.
Dermatology
In order to manipulate the human microbiotas to help treat disease, scientists have to gather information about the identities of microbes and their location and arrangement in different body sites.
Dermatology
Antibiotics can alter the skin microbiota and lead to the emergence of antibiotic resistance. A new study published in Science Translational Medicine.
Gynecology, Pediatrics
Restoring a baby’s natural exposure to maternal vaginal microbes after a C-section birth can normalize the development of the microbiota in newborn.
Dermatology
Immune cells called group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) are responsible for triggering a response when bacteria and viruses breach the skin.
Dermatology, Scientific research
A bacterial strain, called Staphylococcus hominis A9, inhibited the expression of a S. aureus toxin that promotes inflammation in atopic dermatitis.
Dermatology
Some C. acnes strains harbored genes that encoded a molecule similar in structure to a known antibiotic called berninamycin.