gut microbiota
Scientific research
The Gut Phage Database, within more than 140,000 viral species, is a blueprint to guide ecological and evolutionary analysis in future virome studies.
Geriatrics
Microbiota changes in advanced age may not simply be diagnostic of healthy aging, but they could also contribute to health as people become older.
Gastroenterology
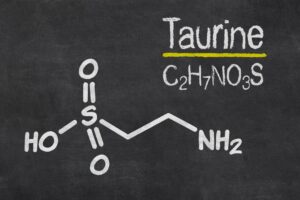
Intestinal infections ‘train’ the gut microbiota to produce taurine, which promotes the growth of protective gut bacteria.
Cardiology
New therapeutic strategies that rely on TLR4 inhibition can counteract the formation of coronary clots in people with cardiovascular disease.
Neuroscience
IL-17 molecules from the gut can influence autoimmune diseases in the central nervous system by regulating the gut microbiota.
Nutrition
Dietary fiber can influence the production of several microbial metabolites that may modify the human gut microbiome and, more in general, health.
Gastroenterology
Different gut metabolites can influence the Cryptosporidium parasite’s growth and invasion of intestinal cells. A new study published in mBio claims.
Oncology
TCGA allows to explore the role of tissue-resident microbiota in various cancer types and identifying predictive microbial biomarkers.
Gastroenterology
Immune responses to the gut microbiota can be used as biomarkers of clinical course in IBD or as targets for the treatment or prevention of the condition.
Gastroenterology, Gynecology
The findings suggest that delivery mode, rather than birth canal exposure, has a strong influence on the composition of the infant microbiota.