Scientific research
Scientific research
The influence of cat ownership on gut microbiota function may affect the health of the owner. A new study published in PlosOne claims.
Scientific research
A new study published in Genome Medicine suggests that international travel poses a high risk by favoring the global spread of antimicrobial resistance.
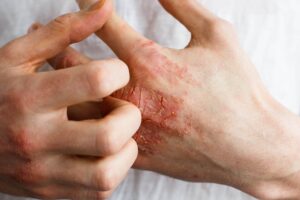
Dermatology, Scientific research
A bacterial strain, called Staphylococcus hominis A9, inhibited the expression of a S. aureus toxin that promotes inflammation in atopic dermatitis.
Scientific research
The way gut bacteria increase their access to nutrients by adhering to food particles, could advance the development of microbiota-based diagnostics.
Scientific research
The Gut Phage Database, within more than 140,000 viral species, is a blueprint to guide ecological and evolutionary analysis in future virome studies.
Scientific research
In a Perspective published in Science, surgeon-scientist Jennifer Wargo explores recent advances in modulating the microbial community within the human gut.
Scientific research
A new study assessed that transplantation of human microbiota into mice durably reshapes the gut microbial community.
Scientific research, Video
PharmaBiome has developed unique technologies to access the entire range of intestinal bacteria. We met Christophe Lacroix, Founder of Pharmabiome.
Scientific research
Researchers have developed an approach that uses bacterial biofilms to increase the ability of the gut microbiota to survive and reside in the gastrointestinal tract.
Scientific research
Researchers have found that the community of bacteria in a person’s gut can alter how well they metabolize drugs.